Highlights
- The engagement and retention of adult sport participants is often overlooked within sport systems and organizations that focus predominantly on youth
- Despite coaches playing a key role in Masters sport, there are no clearly identified pathways into Masters coaching
- Masters athletes are often relegated to the worst practice times and facility resources
- This SIRCuit article examines the research and realities of how the sport system can do a better job supporting lifelong participation, in particular by understanding the needs of Masters, senior athletes and older adults
“Hey! You’ve still got 50+ years of time as an athlete!” I say to my class of university students who study sport and physical activity leadership.
Their stunned response: “What?”
Nobody has ever told them that before. But it’s true.
Adult sport participation is often forgotten. It’s not discussed with the same frequency as youth sport. It’s often not prioritized by organizations and systems within sport, whether that be regarding policies, programming and recruitment, coaching or logistics of facilities use. This is true even of adults who like sport and were heavily involved in sport as children and youth.
We know that sport participation can prevent strain on public health, keep adults and older adults happy and healthy, and encourage them to seek mastery and new experiences. Still, it’s forgotten.
This article examines the research and realities of how the sport system can better support lifelong sport participation beyond youth. Understanding the needs of Masters athletes, seniors athletes, and older adult sport participants is an important consideration.
How we have overlooked Masters athletes and older adults
Much of the research in sport is geared towards high performance or youth sport participation. As the Editor-in-Chief for the International Sport Coaching Journal, I, Bettina (first author) will pick on myself to make this point (though facetiously, as I do not choose which manuscript topics are submitted to the journal). Looking at the most recent issue at the time of writing (Volume 9, issue 3, September 2022), we see the following (generalized) breakdown in the original research publications: 12% coach education, 38% coaching youth, 50% coaching elite, collegiate or professional athletes.
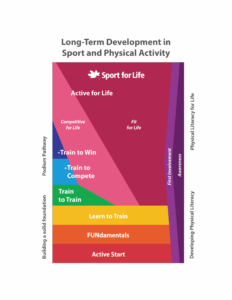
Remarkably, if we survey the model, we can see a parallel focus and how that impacts practice. The LTD uses a rectangular diagram to outline a framework for developmental pathways in sport and physical activity. It depicts a large section devoted to Active for Life, as an alternative to the Podium Pathway towards high performance. This is excellent, as it includes the large number of people (including adults and older adults) who are not on the trajectory toward podium performances at the highest level of sport yet continue to engage in sport and physical activity.
However, while the LTD acknowledges aging adults as an underserviced and under-supported group within the sport and physical activity ecosystem, the information in the framework itself is mostly associated with children, youth, and young adults. The LTD also outlines quality sport and physical activity as developmentally appropriate, well run, safe and inclusive. But the needs and preferences of adults in sport must be understood to create appropriate programming and development, and to make people feel safe and included.
In reality, adult development in sport is often focused on becoming coaches or officials, joining the board of directors for the youth sport team or club, fundraising and volunteering. However, there are many ways in which adults can and should continue their own athletic endeavours. Graduating from high school, college or university should not equate to sport retirement. There are still several decades worth of sport participation and fun to be had. To promote, recruit, and carry-out lifelong sport participation, there need to be supports in place.
The role of coaching in adult-oriented sport
Qualified coaches are important actors that drive much of sport. Indeed, it was suggested to us once that without coaches, there would be no sport. But this is short-sighted, adult sport often exists without coaches. While there are recreational and “beer league” adult sports that most often do not have coaches, we turn the reader’s attention to Masters sport, where coaches can play important roles in the sport system (Callary et al., 2021).
Masters sport is defined as sport events, leagues, and competitions for adults typically over 35 years of age (although this differs based on the sport and can be as young as 18 years old), with sport participants who register (pay), and who practice or train usually towards competitive ends, and who oftentimes have a coach (Young et al., 2018). Within this cohort of more serious-minded adult athletes, effective coaches play an important role in meeting athletes’ psychosocial needs and validating their decision to pursue sport. Athletes, coaches, and those close to the sport system who do not know, or who perhaps underestimate the value of Masters sport, can undermine this role (Callary et al., 2017).
Some question why adults should need coaching. There are ageist assumptions that adults do not improve, and that they are simply there for social and fitness leisure time activity. In our research (Callary et al., 2017), we have found this ageism can lead coaches and athletes to believe that they do not really need to “coach” Masters athletes. That is, that they do not need to develop and prepare training plans, provide feedback, support athlete learning, and invest in quality coach-athlete relationships. Similar assumptions would be absurd within youth sport. Do we still demand quality coaching if young athletes do not become Olympians or professional athletes? Yes, of course. This same logic must apply at the adult sport level. In other words, quality coaching should be an inherent feature of Masters sport and sport for older adults too.
Nonetheless, there are important psychological and social considerations to think through when coaching adults to ensure a Quality Masters Sport Experience (Young et al., 2021). In our book Coaching masters athletes: Advancing research and practice in adult sport (Callary et al., 2021), we outline key psychosocial considerations that emerged from our research program of the last 10 years.
In particular, the book is based on the premise that there are 5 adult-oriented coaching approaches that coaches and athletes alike want, and that are aligned with adult learning principles that will enhance the sport experience (Callary et al., 2021). These adult-oriented coaching approaches have been developed through qualitative in-depth research (such as Callary et al., 2015; 2017; MacLellan et al., 2019) and validated through quantitative analyses.
For example, the Adult Oriented Sport Coaching Survey (AOSCS; Rathwell et al., 2020) defines our 5 themes as follows:
-
Considering the individuality of athletes
- This theme refers to how coaches tailor their approaches to each adult athlete’s experiences and motives when they plan, organize, and deliver practice
-
Framing learning situations
- This theme refers to how coaches prompt and ready their adult athletes to learn through self-discovery, problem-based scenarios, modeling, and assessments
-
Imparting coaching knowledge
- This theme refers to how coaches share their own relevant athletic experience, coaching knowledge, and professional coaching development
-
Respecting preferences for effort, accountability, and feedback
- This theme refers to how coaches adapt their approaches to consider how each adult wishes to be held accountable for working hard and giving effort, and how each adult prefers to receive feedback at practice
-
Creating personalized programming
- This theme refers to how coaches individualize aspects of scheduling (practices and competitions), season-long programming, and support at competitions to an adult athlete’s needs and abilities
These 5 themes, whether applied collectively or used flexibly by coaches of adults, represent an evidence-based palette of coaching practices.
Our ongoing research shows that coaches find different skills and strategies within each of the 5 themes, as well as the theme itself, to be useful and relevant to their coaching. They note that these nuances of adult-oriented coaching approaches can be used as needed, not necessarily in tandem all the time, but instead as a “toolbox” for ongoing coaching practice over time (Callary et al., under review). This is important as coaches may work with the same Masters athletes for many decades. Thus, adopting and trying out new adult-oriented approaches can be particularly important for coaching this cohort, serving to keep things fresh, and possibly sparking further development among coaches.
Keeping in mind the hundreds of things coaches can do and try out with their athletes, Motz and colleagues (2022) indicated that the use of these 5 adult-oriented coaching approaches were particularly associated with positive coach-athlete relationships. Specifically, these researchers found that these approaches accounted for 63% of why Masters athletes feel committed to their coaches, 40% of why Masters athletes feel close to their coaches, and 41% of how Masters athletes see their coaches’ behaviours complementing their own.
When coaches “considered the individuality of their athletes” and “respected adults’ preferences for effort, accountability and being given feedback,” the Masters athletes felt close to their coach, and felt that their coach’s behaviours corresponded to their own. When coaches “created personalized programming,” Masters athletes felt a strong commitment to their coach (Motz et al., 2022). Adult-oriented coaching approaches also address how the coach can create a quality sport experience beyond relationship building. Indeed, when coaches embodied these 5 themes, Motz and colleagues reported how Masters athletes liked going to practice more, and wanted to invest in their sport more, than when coaches used less of these approaches (Motz et al., 2022). The evidence-based research suggests that the coach who uses adult-oriented coaching approaches can be considered an important asset for attracting adults and retaining their investment in sport, enhancing their liking of training, and sustaining commitment.
Nonetheless, there are no identified pathways for coaches into Masters sport. Those who do coach Masters sport tend to be Masters athletes themselves, or coaches of youth who were asked to also coach the Masters group on the side. It is difficult for coaches to see the value of developing themselves as coaches of adults when, for the most part, the system does not place value on such development. There exist no sport-specific coach education and very little other means for coaches to develop their craft and become “qualified” to coach Masters athletes (Callary et al., 2018).
Going forward: Building a better future for older athletes
With the work that we have done, sport organizations around the world have increasingly been calling on us to give workshops and webinars, especially because the coaches in their organizations have asked for such information. The rise in interest is noteworthy. As a result, we have done in-person and online coach education programming in various countries, with a wide range of sports. In these professional development sessions, we outline the 5 adult-oriented coaching approaches and often use surveys such as the AOSCS to have coaches think through the ways in which they apply these approaches or how they could do so.
We were recently commissioned to lead a series of online webinar workshops with a group of Masters coaches from a variety of sports. In these sessions, there were lively discussions around the characteristics of an integral adult sport experience, one that is worthy of investment and generates fulsome benefits for participants. We explored the hallmarks of a Quality Masters Sport Experience (see Young et al., 2021 for a detailed description), and coaches shared amongst each other how they addressed these, allowing them to build a repertoire of ideas from other Masters coaches. In other sessions, we invited coaches (and sometimes their athletes too) to complete the AOSCS and provided them with their scores to identify their strengths and areas for development.
Importantly, these discussions always centre on the coach’s context, and whether these adult-oriented themes (and specific survey items) are or could be useful to them. Coaches do the work to reflect on how they want to develop. The metaphor we used was that we were giving them the paint colours and a palette, but they have the brushes and canvas. They can choose which colours, how much of each colour, and where to blend them to make them their own.
In conclusion, many Masters athletes invest a lot into their sport participation. They want programming and coaching to match their investments of time, energy and money. They will also stop paying for sport if it’s not good. Relegating Masters sport to less ideal practice times (like late night), marginalizing them in facility use, and not providing quality coaching are highly unfortunate oversights. Not supporting coaches to become qualified to effectively work with this cohort is a seriously missed opportunity. Coaches do not know what they do not know, and so when Masters-specific coach education offerings are not present, these coaching opportunities are oftentimes not even on the radar.
Returning to the university students in my class as future (and current) sport leaders, many reflected excitedly on the possibilities of working with adults and older adults, and of staying involved themselves as they age. In this regard, we encourage sport leaders to think about ways in which they can support the professional development of their coaches in Masters sport.
Increasing the focus on training great coaches to work with Masters groups by emphasizing the 5 adult-oriented approaches (in addition to giving training on technical and tactical instruction), is a winning formula. We urge clubs and facilities to better prioritize Masters sport groups by giving them equitable access to training spots. Indeed, sport systems will thrive when adults are given proper consideration.