Le Centre de documentation pour le sport
Le Centre de documentation pour le sport (SIRC) est le centre national de ressources pour le sport au Canada. Depuis plus de 50 ans, il est au service des Canadienes et Canadiens, d’un océan à l’autre, et leur propose les recherches et les ressources les plus récentes.
Votre avis nous intéresse !
Les ressources et les services du SIRC vous semblent-ils utiles ? N’hésitez pas à nous le faire savoir et à nous faire part de vos commentaires dans notre nouveau sondage !
Lisez le SIRCuit du printemps
La publication trimestrielle du SIRC examine en profondeur des sujets pertinents et d’actualité dans le domaine du sport canadien.
Écouter Intelligence sportive dès maintenant !
Le nouveau balado du SIRC est un accès complet aux coulisses du secteur sportif canadien.
Guichet d’emplois du SIRC
Atteignant plus d’un millier de professionnels par jour, les offres d’emploi publiées sur le site du SIRC garantissent que les bons candidats vous trouveront.
Chercher des ressources par catégorie
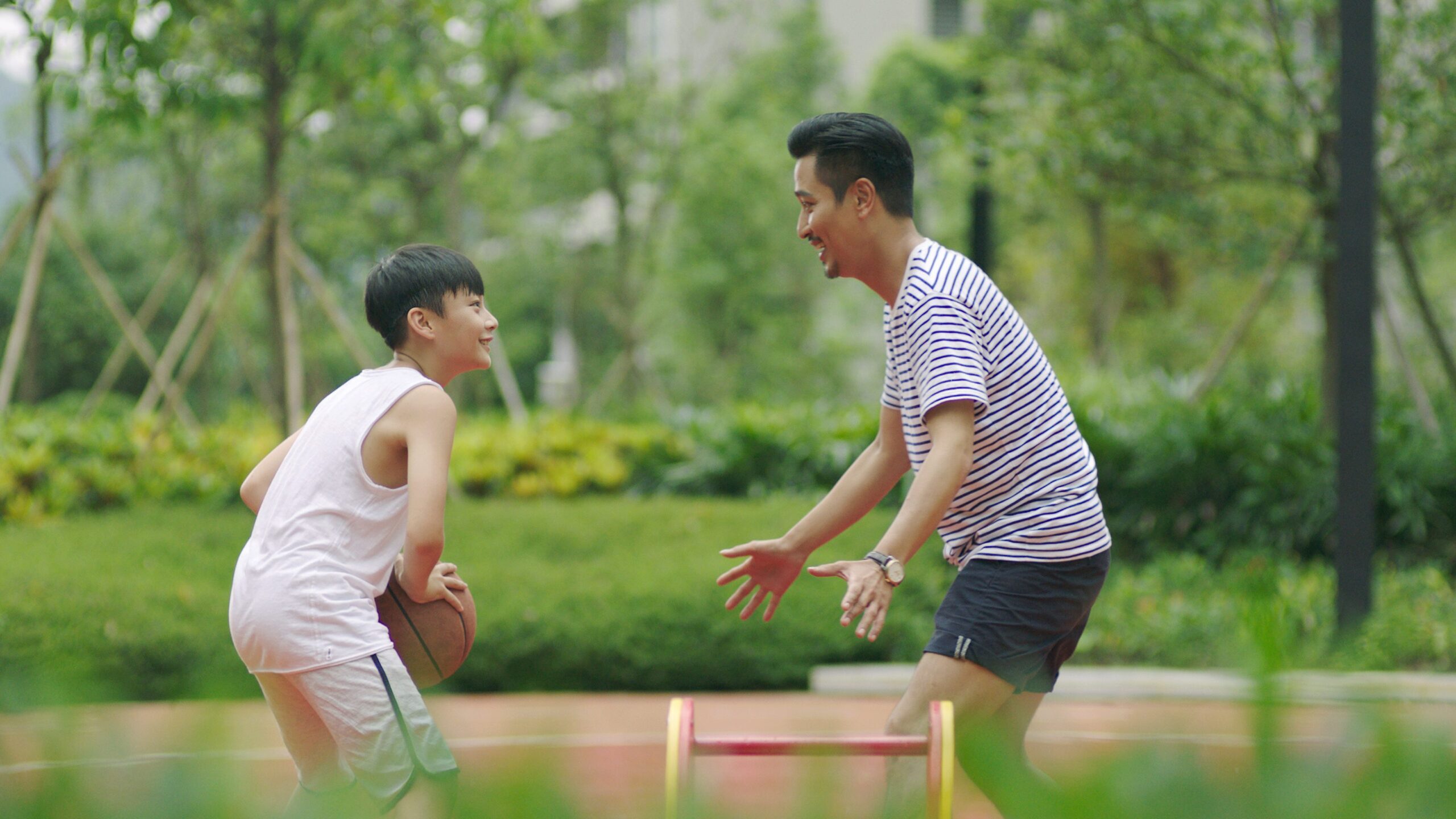
Article en vedette
Quiconque a déjà assisté à un match de soccer pluvieux le samedi ou jonglé avec les horaires des dîners pour s’adapter à l’entraînement de volleyball sait que le sport chez les jeunes ne se fait pas sans les parents. Ils sont les chauffeurs, les meneuses de claque, les bailleurs de fonds et, parfois, les critiques…
Comment nous pouvons vous aider
Depuis plus de 50 ans, le SIRC vise à appuyer l’avancement du sport canadien grâce aux recherches les plus récentes, aux ressources les plus performantes et à un vaste réseau national.
Afficher un emploi
À la recherche de talents ?
Le guichet d’emplois du SIRC offre l’accès à un large bassin de gestionnaires, d’entraîneurs, de bénévoles et plus encore aux organismes œuvrant à tous les niveaux du sport dans le sport canadien. Rejoignant plus d’un millier de professionnels du sport chaque jour, tirez parti du SIRC pour trouver votre candidate idéale ou candidat idéal.
Services du SIRC
Services de recherche du SIRC
Le SIRC offre des services de recherche et d’évaluation personnalisables, de la conception à l’analyse des données, en utilisant des méthodes quantitatives et qualitatives. Adaptez votre projet grâce à nos options flexibles, qu’il s’agisse de services autonomes ou de forfaits complets.
Partagez avec SIRC
Rejoindre le secteur du sport
Le réseau du SIRC s’étend d’un océan à l’autre par le biais du bulletin quotidien du sport canadien, d’articles, de publications SIRCuit, de conférences et autres modes de communication. Devenez un partenaire pour partager vos nouvelles, vos événements, vos emplois et vos connaissances à travers le sport canadien.
S’abonner au quotidien sportif canadien
Les nouvelles vont vite! Livré directement dans votre boîte de réception, le bulletin quotidien virtuel du SIRC vous permettra d’être à l’affut des dernières nouvelles, événements, emplois et connaissances dans le domaine du sport au Canada.